Athlete’s Foot (Tinea Pedis)
Athlete’s Foot (Tinea Pedis):
Causes, Treatment, and Prevention
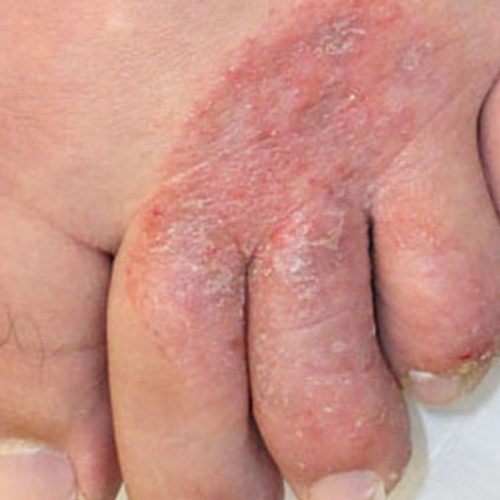
Athlete’s foot, medically known as tinea pedis, is a common fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet, particularly between the toes. It is caused by dermatophyte fungi, which thrive in warm, moist environments. While it is commonly associated with athletes due to frequent sweating, anyone can develop the infection.
Causes and Symptoms
Athlete’s foot is caused by fungal species such as Trichophyton, Epidermophyton, and Microsporum, which invade the outer layer of the skin. These fungi flourish in damp conditions, making sweaty feet, tight shoes, and poor foot hygiene key risk factors.
Common symptoms of athlete’s foot include:
- Itching, burning, or stinging between the toes
- Dry, scaly, or cracked skin on the soles of the feet
- Blisters or ulcers in severe cases
- Thickened, discoloured, or crumbly toenails if the infection spreads
The infection can vary in severity, ranging from mild itching to painful, cracked skin that increases the risk of secondary bacterial infections.
Treatment Options
Several treatment options are available for athlete’s foot, ranging from over-the-counter remedies to prescription medications:
1. Over-the-Counter Antifungal Medications
- Topical antifungal creams, sprays, or powders containing clotrimazole, terbinafine, miconazole, or tolnaftate are effective for mild cases.
- These treatments should be applied for at least one to two weeks after symptoms disappear to prevent recurrence
- There is also an effective once only treatment for milder cases which can be reapplied after 2 weeks if the symptoms persist
- Make sure to treat all shoes with antifungal powder or sprays as well as your feet to prevent reinfection
2. Prescription Treatments
- In cases where the infection is severe or does not respond to over-the-counter medications, a doctor may prescribe stronger topical or oral antifungal medications such as fluconazole, itraconazole, or terbinafine tablets.
- If secondary bacterial infections occur, antibiotics may also be required.
3. Home Remedies and Natural Treatments
- Soaking feet in Epsom salt baths can help reduce fungal growth.
4. Proper Foot Care
- Keeping feet dry and clean is crucial for effective treatment.
- Changing socks regularly and allowing shoes to air out can prevent the infection from worsening. Rotating your shoes, i.e not wearing the same pair of shoes 2 days running, will allow shoes to dry out properly.
- Washing socks inside out on a 60 degree wash can kill off the fungi laying within the sock fibres
Prevention Strategies
Preventing athlete’s foot requires maintaining proper foot hygiene and avoiding exposure to fungal spores. The following steps can help reduce the risk of infection:
1. Keep Feet Dry
- Dry feet thoroughly after bathing, especially between the toes.
- Wear moisture-wicking socks and breathable shoes.
- Wearing nature fibre socks such as bamboo
2. Use Antifungal Powders or Sprays
- Applying antifungal powder or spray can help keep feet dry and free from infection.
3. Change Socks and Shoes Regularly
- Rotate shoes to allow them to dry out completely.
- Avoid wearing tight, non-breathable shoes for extended periods.
Conclusion
Athlete’s foot is a common yet treatable condition that can cause discomfort if left unmanaged. By maintaining good foot hygiene, using antifungal treatments when necessary, and taking preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of infection and prevent recurrence. If symptoms persist despite treatment, consulting a foot health practitioner is recommended to rule out complications or alternative skin conditions.